In an interactive map, FOSA provided a geographic breakdown of global DFOS installations in more than 75 countries. Key insights include:
- China had more deployments than any other nation with roughly 11.3% of all identified installations, followed closely by Germany at 9.4%. The United States came in third with roughly 6.5%, and South Korea was fourth with 4.8% of installations.
- Assets most frequently monitored using DFOS included power cables (22.2%), tunnels (20%), pipelines (13.5%) and perimeters (8.4%).
- The more than 1,300 identified installations span more than 20,000 miles in length (33,300 km).
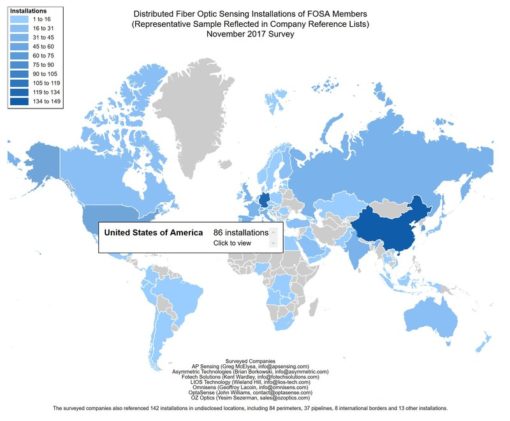
FOSA Map Screenshot
“According to our data, the United States is well behind China and Germany in terms of total deployments of fiber optic sensing. We are committed to raising awareness of this powerful technology, which can help bring U.S. infrastructure and asset security into the 21st century,” said Mark Uncapher, Director of FOSA.
Fiber optic sensing enables highly precise remote monitoring of physical assets, including power cables, pipelines, railways, international borders and critical infrastructure.
“With fiber optic sensing, hundreds of miles of highway can be monitored for accidents and traffic flows,” Uncapher said. “Power cable faults and pipeline leaks can be detected and located instantly, and footsteps can be heard on a perimeter in the middle of the night. They are all detectable through fiber optic sensing.”
Industries that already leverage DFOS include transportation, energy, security, oil and gas, and defense.
The release of the FOSA interactive map and corresponding data builds on the organization’s ongoing effort to promote awareness of fiber optic sensing technology.
The new data reflects information provided by FOSA member companies’ reference lists. Reference lists are comprised of projects determined by a company to be representative of its total deployments.
About the Fiber Optic Sensing Association:
 The Fiber Optic Sensing Association is a non-profit organization with the mission of educating industry, government and the public on the benefits of fiber optic sensing.
The Fiber Optic Sensing Association is a non-profit organization with the mission of educating industry, government and the public on the benefits of fiber optic sensing.


